Analytical Simulation for Acceptance of Maximum Serious Injuries that can be handled at Disaster Base Hospitals
概説
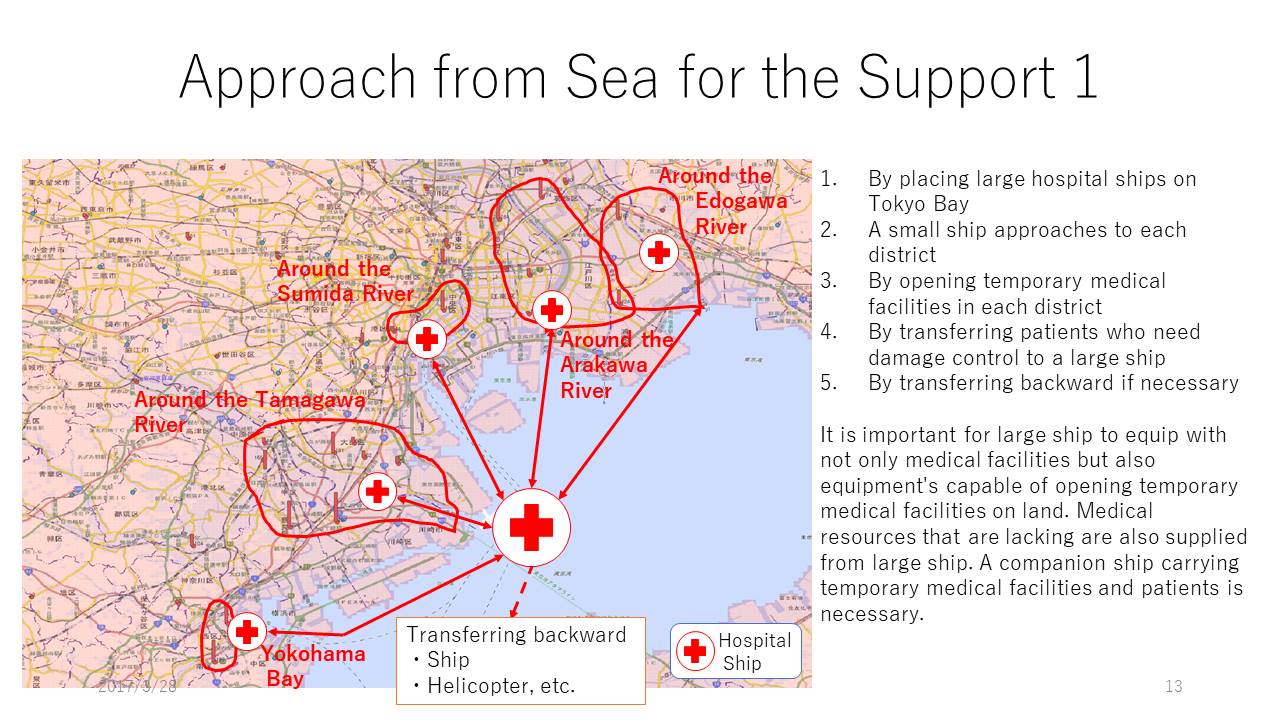
Simulation of SIP activity and damage estimation system Simulation analysis on earthquake under the capital city Distribution of seriously injured patients outbreak and accommodation at disaster base hospital Distribution of patients who can not be accommodated at disaster base hospital Consideration of medical support by approach from the sea For the seismic intensity distribution and distribution of seriously injured patients, the data provided by research results of SIP are used. The patient's accommodation is simulated assuming that the bed occupancy rate in peacetime is assumed to be 80% and patients occurred are accommodated in 20% vacant. The patient to be transported means patient that needs to be transported to another medical institution because the disaster base hospital can not accommodate due to fully occupied beds. The content of this presentation is based on research results of the SIP (Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program) "Strengthening Resilient Disaster Prevention and Reduction Function" of "Integrated Science and Technology · Innovation Conference" (Administrative Corporation: JST).
目次
Social Simulation
Areas that clarify social phenomena (economics, transportation, public health, crisis management, etc.) through simulation
Background of the simulation
Use of computer simulation started in the 1960s.
Diffusion in the 1990's by computer evolution
Purpose of simulation
Understanding phenomena (as is) and anticipation / prediction (to be)
Simulation technology
Mathematical analysis and study (classical method)
Analysis and study by reproducing social phenomena in artificial society on computer
Various methods such as geographic information analysis, network analysis, agent base, etc.
基本情報
| 発表者 | Manabu Ichikawa (Department of Health Crisis Management National Institute of Public Health ) |
|---|---|
| ページ数 | 14 ページ |
| 発行年 | 2017/08/28 |
| 情報更新日 | 2017/09/16 |